Venture Capital
Venture capital (VC) represents a subset of private equity, focusing on providing financial support to startups and small enterprises that show promise for substantial growth over time. This funding is typically sourced from individual investors, investment banks, and financial institutions. Additionally, venture capital may include the provision of technical or managerial expertise to assist the companies in their development.
Types of Venture Capital
Pre-seed
Seed Funding
Early-Stage Funding
Venture Capital Pros & Cons
Pros
- Stimulating innovation: Venture capital fuels innovation by funding projects like Tesla, which revolutionized the electric vehicle industry and encouraged sustainability.
- Supporting startups: Companies like Airbnb received venture capital support, allowing them to grow into global giants, creating jobs and new business models.
- Job creation: Startups supported by venture capital create jobs, as seen with companies like Amazon, which has a vast workforce.
- Development of new technologies: Investments in startups like SpaceX advance technologies, leading to breakthroughs in space exploration and transportation.
Cons

- High level of risk.
Venture capital investment is inherently risky due to the nature of startups. These companies often have unproven business models and face a competitive landscape. For instance, statistics indicate that approximately 90% of startups fail. Investors can lose their entire investment in these cases.
Example: Consider the case of Juicero, a startup that received significant venture capital funding to develop a high-tech juicing machine. The product faced criticism for being over-engineered and overpriced, ultimately leading to the company’s closure and investor losses. - Short-term approach.
Venture capitalists typically seek rapid returns on their investments. This can put pressure on startups to prioritize short-term profitability over long-term sustainability. Startups may be forced to cut corners or focus on quick wins, potentially neglecting important aspects like ethical considerations or product quality.
Example: Some ride-sharing companies, in their pursuit of rapid growth, faced controversies related to labor practices, safety, and regulatory compliance, highlighting the potential downsides of a short-term focus. - Influence on entrepreneurs.
Venture capitalists often have significant control over startups they invest in, including board seats and decision-making power. This influence can lead to conflicts between the interests of investors and the vision of the entrepreneurs.
Example: Snap Inc., the parent company of Snapchat, faced challenges when its founders resisted certain changes proposed by investors, highlighting the tension that can arise between entrepreneurs and venture capitalists. - Support for highly specialized industries.
Venture capital tends to concentrate heavily in technology-related sectors, neglecting other important areas such as education, healthcare, and the environment. This can lead to underinvestment in critical sectors.
Example: While technology startups receive significant funding, nonprofits and companies focused on solving pressing global issues, like clean energy startups, often struggle to secure venture capital support. - High inequality.
Venture capital investments are often concentrated in geographic hubs like Silicon Valley, exacerbating economic inequality by neglecting startups from less developed regions. This can lead to a “rich get richer” dynamic.
Example: Startups in emerging economies with promising ideas may struggle to attract venture capital attention, perpetuating regional disparities in innovation and economic development. - Short-term thinking.
Investors often prioritize financial performance metrics like revenue growth and profitability, sometimes at the expense of broader societal contributions or long-term sustainability.
Example: Some companies may prioritize aggressive cost-cutting measures, potentially leading to layoffs and negative social impacts, in their pursuit of short-term financial success. - Concentration of risk.
Despite the high risks involved, venture capitalists often focus their investments on a small number of startups, making their portfolios vulnerable to significant losses if any of these projects fail.
Example: A venture capital firm heavily invested in a single industry or technology may suffer substantial losses if that industry experiences a downturn or if a disruptive technology emerges.
Challenges

- Lack of Diversity: The venture capital industry is not sufficiently diverse in terms of investors and startup representatives. Venture capital has often remained male-dominated, and there is an underrepresentation of women and minorities among startup representatives. The underrepresentation of women and minorities among both investors and entrepreneurs can result in a narrow focus on certain types of startups.
- Lack of transparency: Some aspects of venture capitals may have little transparency, which may cause doubts and concerns among startups and the public. The secretive nature of some venture capital deals can create uncertainty and mistrust among startups and the public.
- Corporate interests: In case of attracting investments from large corporations, startups may face the problem of conflict of interest and loss of independence. When large corporations invest in startups, there’s a risk of conflicts of interest and loss of startup independence, affecting innovation and creativity.
- Investing in hot sectors: The venture capital industry often tends to invest in trendy and popular sectors, which may lead to market saturation and limit the diversity of investments.The venture capital industry’s tendency to follow trends can lead to saturation in certain markets, stifling diversity and competition.
Venture Capital in Gaming
In 2020-2021, the gaming industry has been developing at a rapid pace, with its revenues soaring to tens of billions of dollars and exceeding pre-pandemic analyst expectations. In 2022, after the abolition of lockdowns and due to a general economic downturn as well as shifting purchase priorities, the video game market lost 4.3% of its profits. However, analysts suggest the gaming market is facing a “bright future” with steady growth in terms of both revenue and user numbers.
Venture capital plays a critical role in funding and supporting game development projects. Here are a few key reasons why venture capital is paramount in this industry:
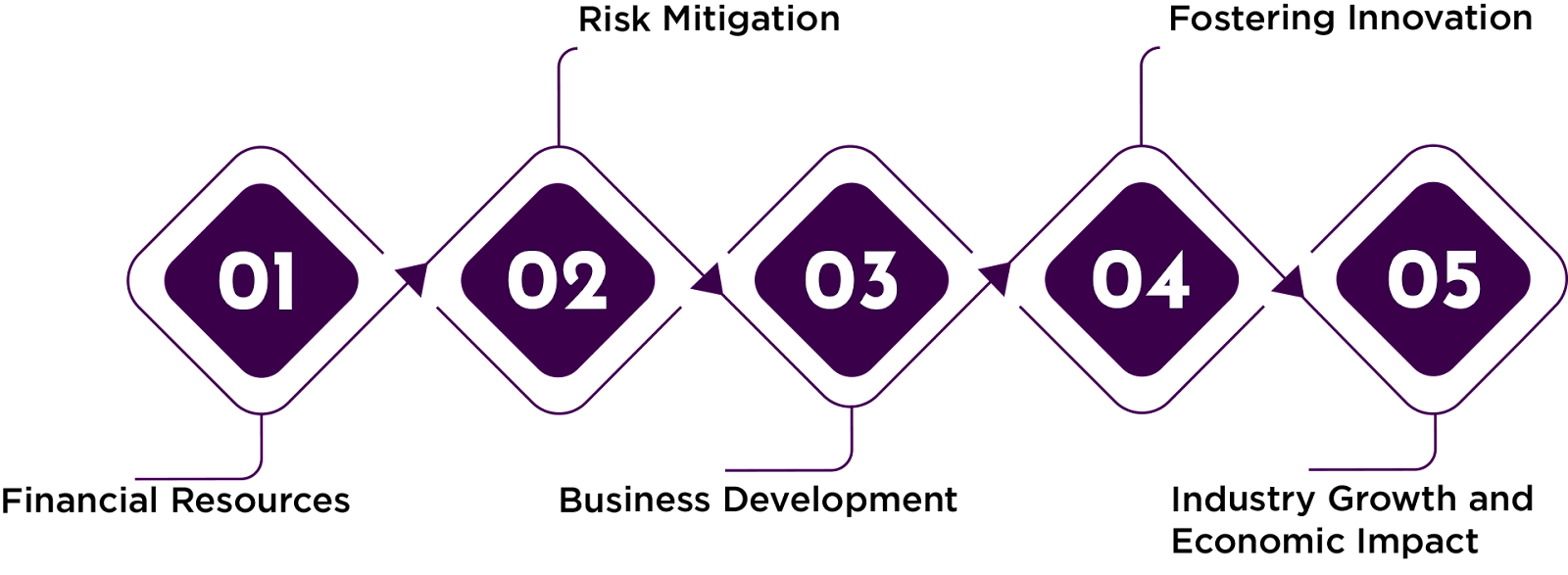
- Financial Resources — Game development requires significant financial investment: from hiring talented people to acquiring cutting-edge technology and marketing the final product. Venture capital companies provide the necessary capital to cover these expenses, allowing developers to focus on creating innovative and engaging games without being burdened by financial constraints.
- Risk Mitigation — Game development is inherently risky and does not guarantee success. Venture capital firms specialize in assessing risks and rewards, using their expertise to assess market trends, analyzing target audiences, and identifying potential barriers. By collaborating with venture capital investors, game developers receive valuable guidance and mentorship, reducing the risks associated with their projects’ implementation.
- Business Development — Venture capital companies not only provide financial assistance but also contribute to business development in gaming projects. Through their extensive networks and industry connections, venture capitalists open doors to valuable partnerships, distribution channels, and marketing opportunities. Their experience in business scaling can help game developers grow their studios, expand their teams, and sprout into new markets.
- Fostering Innovation — The gaming industry thrives on innovation and creativity, and venture capital plays a vital role in fostering these qualities. Venture capital companies are actively looking for innovative ideas, unique game mechanics, and new approaches to storytelling. By investing in game projects, VCs provide developers with the funding needed to take risks, experiment with novel concepts, and push the industry boundaries. This financial support encourages them to innovate, resulting in groundbreaking games that captivate gamers around the world.
- Industry Growth and Economic Impact — Venture investments in game development projects contribute to the overall growth of the gaming industry that, in turn, makes significant contributions to the local economy by generating billions of dollars in revenue and creating new jobs. By supporting game developers, VCs are driving this growth by allowing studios to expand their operations, hire talent, and develop more ambitious projects. The positive economic impact of the gaming industry is enhanced by venture capital investments.
GameDev Companies funded by VCs: Successful Cases
Success stories where venture capital investments have played a key role in propelling startups to greater heights abound in the gaming industry. Let us take a look at some notable examples.
Accel Partners and Supercell Partnership Leading to Clash of Clans
This mobile game development company based in Finland is an exceptional success story. Backed by venture capital investments from firms such as Accel Partners and Index Ventures, Supercell has achieved global recognition with prominent hits such as Clash of Clans and Clash Royale. The company’s innovative approach to game design, combined with strategic investments, led to its acquisition by Tencent for a staggering $8.6 billion in 2016.
Tencent Investments into Epic Games Resulting in Fortnite
The developer of the immensely popular game Fortnite has also been a huge success thanks in part to venture capital investment. Tencent, a major Chinese investment company, invested $330 million into Epic Games in 2012, allowing the company to expand its reach and development capabilities. Fortnite’s unprecedented success has propelled Epic Games’ valuation to over $15 billion in 2018.
Roblox backed up by Meritech Capital Partners
An online gaming platform and game creation system that has amassed an enormous user base and achieved remarkable success backed by venture capital. The company raised over $335 million in funding, including investments from Meritech Capital Partners and Index Ventures. With a unique approach to driving user-generated content and forming a bustling community of both players and developers, Roblox became a cultural phenomenon and has gone public with a valuation in excess of $40 billion in 2021.
$400 Million Injection from Silver Lake Partners to Unity
Game engine creator Unity revolutionized game development with its powerful and accessible tools. The company received significant venture capital investments, including a $400 million injection from Silver Lake Partners in 2017. The Unity engine has been instrumental in the creation of many popular titles such as Pokémon Go, Among Us, and countless others. In 2020, Unity Technologies went public with a market valuation of around $13 billion.
Accomplishments of the cases above demonstrate the vital role that venture capital plays in driving innovation, promoting growth, and generally shaping the landscape of the gaming industry.