![Largest Gaming Companies: Ranked by Revenue [2024] Largest Gaming Companies: Ranked by Revenue [2024]](https://data40.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Header-6.jpg)
The gaming industry is a colossal global market, continually expanding in both technological advances and financial growth. This article explores the largest publicly traded gaming companies in 2024, ranked by revenue. It delves into each company’s origin, flagship products, and the business strategies that have led them to dominate the market. The gaming industry is more than just entertainment; it’s a powerful economic force. It not only creates jobs but also pushes the envelope on technology and innovation. The importance of the gaming industry can be seen in its rapid growth and its ability to generate substantial revenue.
| Company | CEO | Established | Headquarters | Employees | Revenue |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
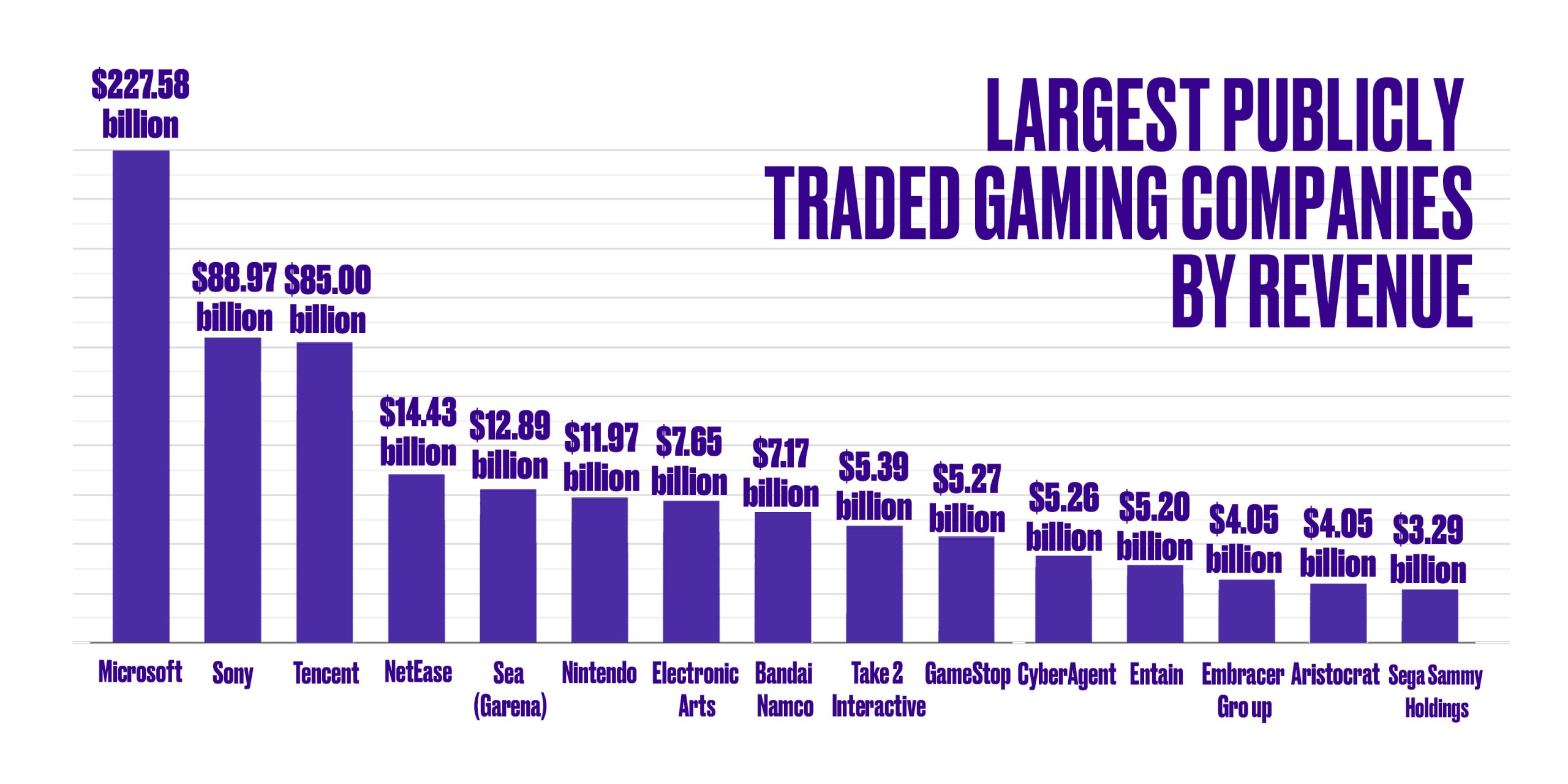
 | Satya Nadella | April 4, 1975 | Redmond, Washington, United States | 221,000 (2023) | $227.58 B |
| | Kenichiro Yoshida | May 7, 1946 | Kōnan, Minato, Tokyo, Japan | 113,000 (2023) | $88.97 B |
 | Pony Ma | November 7, 1998 | Tencent Binhai Mansion, Nanshan District, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China | 112,771 | $85.00 B |
 | Ding Lei | June, 1997 | Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China | 31,119 | $14.43 B |
 | Forrest Li | 2009 | 1 Fusionopolis Place, #17-10, Galaxis, Singapore 138522 | 67,000 | $12.89 B |
 | Shuntaro Furukawa | September 23, 1889 | 11–1 Kamitoba Hokodatecho, Minami-ku, Kyoto, Japan | 7,317 (2023) | $11.97 B |
 | Andrew Wilson | May 27, 1982 | Redwood City, California, U.S. | 12,900 | $7.65 B |
 | Mitsuaki Taguchi | September 29, 2005 | Sumitomo Fudosan Mita Building, Minato, Tokyo, Japan | 10,562 (2023) | $7.17 B |
 | Strauss Zelnick | September 30, 1993 | New York City, US | 11,580 | $5.39 B |
 | Ryan Cohen | 1984 | Grapevine, Texas, U.S. | 27,000 | $5.27 B |
 | Susumu Fujita | March 18, 1998 | Abema Towers, 150-0042 Shibuya, Tokyo, Japan | 6,340 (2022) | $5.26 B |
 | Stella David | 2004 | Douglas, Isle of Man | 23,650 | $5.20 B |
 | Lars Wingefors | 2011 | Karlstad, Sweden | 15,218 | $4.05 B |
 | Trevor Croker | 1953 | Sydney, Australia | 6400 | $4.05 B |
 Sega Sammy Holdings Sega Sammy Holdings | Haruki Satomi | October 1, 2004 | Sumitomo Fudosan Osaki Garden Tower, Tokyo, Japan | 7,535 | $3.29 B |
Top biggest gaming companies
Microsoft
Revenue: $227.58 B
Country: USA
Founded: 1975
Founded by Bill Gates and Paul Allen, Microsoft has evolved into a dominant force in the global technology and gaming industries. Their gaming division is best known for the Xbox console series, which has been a significant player in the gaming market since its introduction in 2001. Popular games like “Halo” and recent acquisitions, including Bethesda Softworks, have been pivotal in driving their revenue. Microsoft promotes its games and consoles through a combination of direct marketing, partnerships with other entertainment industries, and comprehensive digital marketing strategies. Their business model, which includes hardware sales, software sales, and a strong emphasis on subscription services like Xbox Game Pass, allows them to maintain a steady revenue stream while expanding their gaming ecosystem.
Sony
Revenue: $88.97 B
Country: Japan
Founded: 1946
Sony, founded by Akio Morita and Masaru Ibuka, has a vast portfolio that spans various electronics, entertainment, and gaming sectors. The PlayStation brand, introduced in 1994, has been central to Sony’s success in the gaming industry. Iconic games such as “The Last of Us,” “God of War,” and the “Uncharted” series have not only received critical acclaim but have also contributed significantly to their financial success. Sony utilizes a robust marketing strategy that includes aggressive advertising, strategic alliances, and exclusive content to promote their games and consoles. Their business model is heavily reliant on hardware sales, proprietary software, and network services that engage their extensive user base.
Tencent
Revenue: $85.00 B
Country: China
Founded: 1998
Founded by Ma Huateng, also known as Pony Ma, Tencent is a Chinese conglomerate with a substantial stake in the global digital and gaming market. It is known for owning WeChat and a significant portfolio in video gaming through investments in various major gaming companies worldwide. Popular games like “Honor of Kings” and their partnership in “League of Legends” have been highly lucrative. Tencent’s strategy includes not only developing its own games but also acquiring stakes in established gaming companies to broaden their influence across the industry. They promote their games through social media integration, competitive gaming leagues, and cross-promotion with other media properties. The business model focuses on microtransactions, subscriptions, and advertising within their gaming platforms, optimizing the monetization of their extensive user base.
NetEase
Revenue: $14.43 B
Country: China
Founded: 1997
Founded by Lei Ding, NetEase is one of China’s leading internet and video game companies. The company has gained significant recognition through its development of popular games such as “Fantasy Westward Journey” and “Ghost Story,” which are major hits within China. Over the last two years, NetEase has focused on incorporating advanced AI technologies to enhance user engagement and game personalization. They also expanded into cloud gaming to broaden accessibility. NetEase promotes its games through a combination of social media marketing, strategic partnerships with Western game developers, and large-scale online community engagement. Their business model is primarily based on free-to-play games with in-app purchases and a growing emphasis on subscription services, which has proven to be very effective in generating sustained revenue.
Sea (Garena)
Revenue: $12.89 B
Country: Singapore
Founded: 2009
Sea Limited, through its digital entertainment arm Garena, has made significant strides in the gaming industry, particularly in Southeast Asia. Founded by Forrest Li, Garena is renowned for publishing “League of Legends” in the region and for its blockbuster mobile game, “Free Fire.” In the past two years, Garena has invested heavily in mobile gaming technologies, including the integration of augmented reality features to enhance gameplay experiences. The company promotes its games through influencer partnerships, competitive esports tournaments, and localized marketing strategies tailored to the diverse Southeast Asian market. Garena’s business model leverages the free-to-play format with in-game purchases, which has been highly successful, particularly in markets where paid game models are less common.
Nintendo
Revenue: $11.97 B
Country: Japan
Founded: 1889
Founded as a playing card company, Nintendo was transformed under the guidance of visionaries like Fusajiro Yamauchi and later Hiroshi Yamauchi. It is now globally recognized for its innovative approach to gaming, with iconic franchises such as Mario, Zelda, and Pokémon. Over the last two years, Nintendo has continued to innovate by enhancing its hardware with the launch of the Nintendo Switch OLED model and expanding its mobile presence. Technological innovations have included the development of Nintendo Switch Online, augmented reality applications in games like “Pokémon Go,” and exploring cloud gaming. Nintendo promotes its games through a nostalgia-driven marketing approach, leveraging its long-standing brand identity, and through unique interactive experiences in theme parks and merchandise. Their business model includes hardware sales, game sales, and increasingly, online subscription services, creating a robust and diversified revenue stream.
Electronic Arts (EA)
Revenue: $7.65 B
Country: USA
Founded: 1982
Founded by Trip Hawkins, Electronic Arts has established itself as a powerhouse in the gaming world, particularly known for its sports titles like FIFA, Madden NFL, and the Battlefield series. In the past two years, EA has invested in cloud gaming technology and advanced AI to create more realistic and engaging gameplay experiences. These technologies also allow for the personalization of gameplay and dynamic game environments. EA promotes its games through high-profile partnerships with sports leagues and athletes, extensive digital marketing, and community engagement via social media and live events. The company’s revenue strategy revolves around a mix of premium game sales, a strong focus on recurring revenue through in-game transactions, and subscription services such as EA Play, which have been crucial in sustaining its financial success.
Bandai Namco
Revenue: $7.17 B
Country: Japan
Founded: 2006 (merger)
Formed from the merger of Bandai and Namco, Bandai Namco is not only involved in video gaming but also other entertainment sectors such as toys and amusement facilities. Known for popular titles like Tekken, Dark Souls, and the Dragon Ball series, Bandai Namco has been innovating with virtual reality (VR) and mixed reality (MR) technologies to provide immersive gaming experiences. Over the last two years, they have integrated these technologies particularly in their arcade and home console games. The promotion strategy of Bandai Namco includes leveraging their extensive IP catalog across various media, engaging fans with cross-platform storytelling, and organizing global esports tournaments. Their financial approach focuses on diversifying revenue streams, including game sales, merchandise, and theme park operations, which help maintain their profitability and market position.
Take-Two Interactive
Revenue: $5.39 B
Country: USA
Founded: 1993
Founded by Ryan Brant, Take-Two Interactive is best known for its subsidiary labels, Rockstar Games and 2K, under which it releases blockbuster titles like Grand Theft Auto, Red Dead Redemption, and the NBA 2K series. In recent years, Take-Two has embraced next-generation graphics technology and AI to enhance the narrative and visual fidelity of its games. Additionally, they have explored user-generated content tools in games like GTA Online, which have significantly extended the lifecycle of their games. Take-Two’s promotional activities are heavily reliant on their strong narrative-driven marketing, celebrity endorsements, and viral marketing campaigns. Their commercial framework is built around maximizing earnings through direct game sales, expansive downloadable content, and an increasing reliance on virtual goods and services, which collectively form a sustainable profit model.
GameStop
Revenue: $5.27 B
Country: USA
Founded: 1984
GameStop, initially a small retailer founded by Leonard Riggio, Gary Kusin, and Daniel DeMatteo, has evolved into a major player within the gaming retail industry. While primarily known for its brick-and-mortar stores selling video games, consoles, and gaming accessories, its most popular offering has been its extensive variety of new and used video games which cater to a wide demographic. In the last two years, GameStop has ventured into digital sales and the blockchain space, exploring NFTs and digital asset technologies to adapt to the evolving market. The company promotes itself through aggressive pricing strategies, exclusive deals, loyalty programs, and a strong online community presence. The financial architecture of GameStop is transitioning from traditional retail towards a blend of physical and digital distribution channels, aiming to capitalize on the growing trend of digital gaming consumption.
CyberAgent
Revenue: $5.26 B
Country: Japan
Founded: 1998
CyberAgent, founded by Susumu Fujita, started as an Internet advertising business and quickly expanded into the gaming and media sectors. The company’s gaming division is renowned for popular mobile games like “Granblue Fantasy” and “BanG Dream! Girls Band Party!” which have garnered a substantial following in Japan and beyond. Over the past two years, CyberAgent has invested in AI-driven game development tools and personalized advertising technologies to enhance user engagement and improve game monetization. The company utilizes a multifaceted promotional strategy that includes television advertising, online campaigns, and collaborations with anime series to increase visibility. CyberAgent’s economic strategy emphasizes microtransactions and ad revenues within their mobile games, securing continuous revenue flow and user base expansion.
Entain
Revenue: $5.20 B
Country: United Kingdom
Founded: 2004 (as GVC Holdings)
Entain, previously known as GVC Holdings and led by founding CEO Kenny Alexander, is a major global sports betting and gaming group. While not traditionally known for video games, Entain’s portfolio includes a range of online gaming and sports betting brands like Ladbrokes, Coral, and bwin. The most significant revenue generators have been their online sportsbooks and casino games, which are among the most recognized in the industry. Recently, Entain has focused on integrating immersive technologies such as virtual reality into their betting experiences to enhance user engagement. The company promotes its services through high-profile sponsorships, targeted online advertising, and strategic partnerships with major sports leagues. Entain’s commercial strategy revolves around leveraging cutting-edge technology to offer new forms of gaming and betting experiences, maintaining a robust platform for recurring revenue through user bets and gaming services.
Embracer Group
Revenue: $4.05 B
Country: Sweden
Founded: 2008 (originally as Nordic Games Licensing AB, later rebranded)
Founded by Lars Wingefors, Embracer Group has grown through an aggressive strategy of acquisitions, rapidly expanding its portfolio of studios and intellectual properties. It owns several well-known subsidiaries such as THQ Nordic, Gearbox Entertainment, and Deep Silver. Popular titles under its umbrella include “Saints Row,” “Metro Exodus,” and “Borderlands.” In the past two years, Embracer Group has focused on integrating cross-platform play capabilities and enhancing cloud gaming technologies to broaden their market reach. The company promotes its diverse game lineup through targeted digital campaigns, strategic partnerships with other media companies, and participation in major gaming expos and conventions. Embracer Group’s commercial operations rely on a revenue generation strategy that includes leveraging a broad portfolio of games to cater to varied gamer demographics, which helps in maximizing sales and distribution efficiency.
Aristocrat
Revenue: $4.05 B
Country: Australia
Founded: 1953
Aristocrat, founded by Len Ainsworth, initially focused on manufacturing slot machines and has evolved into a leading name in the gaming machine industry and a burgeoning presence in the digital gaming space. Their most popular products include casino gaming machines like “Queen of the Nile” and mobile games such as “Raiders of the Hidden Realm” and “Heart of Vegas.” Over the last two years, Aristocrat has ventured into virtual reality slots and continued enhancing their digital platform capabilities to attract a broader online audience. The company utilizes direct marketing, participation in international gaming fairs, and digital channels to promote its products. Aristocrat’s revenue dynamics are based on a combination of sales from physical gaming machines and a growing focus on digital games, which provide recurrent revenue through in-app purchases and subscriptions.
Sega Sammy Holdings
Revenue: $3.29 B
Country: Japan
Founded: 2004 (merger of Sega and Sammy)
Sega Sammy Holdings was created from the merger of two Japanese giants: Sega, a leading video game developer, and Sammy, known for pachinko machines. Sega, originally founded by Martin Bromley and Richard Stewart in 1960, is famed for iconic franchises such as “Sonic the Hedgehog,” “Yakuza,” and “Total War.” In recent years, Sega Sammy has embraced cloud gaming technology and advanced AI to deliver more immersive and interactive gaming experiences. The company’s promotional activities include leveraging their strong IP lineup in various multimedia formats, nostalgic marketing for their classic games, and robust participation in gaming conventions. Sega Sammy’s revenue framework involves a mix of earnings from pachinko machine sales and a strong emphasis on game development and digital content distribution, ensuring diversified income streams that capitalize on both legacy and modern gaming trends.
Future Trends in the Gaming Industry
The video game industry, particularly among publicly traded companies, is witnessing several key development trends in 2024 that reflect its dynamic nature and the evolving preferences of consumers. Here are the significant trends shaping the sector this year:
1. Increased Focus on Subscription Models
Publicly traded companies are increasingly investing in subscription services as a stable revenue source that also provides value to gamers. Services like Xbox Game Pass and PlayStation Now offer gamers a vast library of games at a fixed monthly rate, encouraging longer engagement periods and reducing the reliance on individual game sales. This model is attractive to consumers seeking variety and affordability, and it benefits developers by broadening their audience.
2. Expansion of Cloud Gaming
Cloud gaming continues to grow, driven by improvements in cloud infrastructure and faster internet speeds. Companies like Microsoft, Google, and Amazon are enhancing their cloud gaming platforms, such as xCloud, Stadia, and Luna, respectively. This technology allows players to stream games directly to their devices without needing powerful hardware, which opens up high-quality gaming to a broader audience. Publicly traded companies are capitalizing on this trend to tap into markets previously constrained by hardware costs.
3. Enhanced Focus on Mobile Gaming
Mobile gaming is not slowing down; if anything, it’s becoming more integral to the strategies of major gaming companies. With the global proliferation of smartphones, companies are focusing on mobile versions of successful PC and console titles to capture the vast mobile gaming market. This trend is evident with the success of games like “Call of Duty Mobile” and “League of Legends: Wild Rift,” which have expanded the reach of these franchises significantly.
4. Diversification into New Realities
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are receiving renewed interest as technology advances reduce previous barriers to entry, such as high costs and limited content. Companies like Sony and Facebook (through Oculus) are investing heavily in next-generation VR systems that offer more immersive and interactive gaming experiences. Additionally, AR games continue to attract users who prefer more casual and accessible gaming experiences, as seen with the ongoing popularity of titles like “Pokémon GO.”
FAQ
The primary revenue sources vary, from digital sales and subscriptions to in-game purchases and advertising.
Acquisitions allow gaming companies to diversify their portfolios, acquire new technologies, and tap into new customer bases.
The global market has allowed these companies to reach wider audiences, leading to increased sales and diversification of revenue streams.