The gaming industry is rapidly evolving, shifting from Web2 to Web3, requiring a rethinking of approaches to creating and maintaining game economies. P2E game tokenomics represents a key direction in this evolution. However, developing a sustainable and functional economy in a Web3 environment faces unique challenges that do not exist in Web2.
It is crucial to consider these features when building game ecosystems to prevent inflation, asset outflow, and other problems that past P2E projects have encountered.
Challenges of Transitioning from Web2 to Web3
The game economy in Web2 typically functions as a closed system, where the game company controls all aspects—from the creation and distribution of in-game assets to managing their value. Web3 opens new opportunities for users, including full ownership of digital assets and the ability to monetize them outside the game, which creates difficulties for game companies. It is important to consider these features when building game ecosystems to prevent inflation, asset outflow, and other issues that P2E projects face.
P2E Tokenomics: What It Is and How It Works
P2E tokenomics can radically change the traditional approach to game monetization. Existing tokenomics models allow game developers to create a sustainable and fair economy where players can earn real money for their time and effort invested in the game. At the same time, additional tools are created, allowing not only players but also developers and investors to earn. The success of P2E games largely depends on proper tokenomics management, which requires a deep understanding of not only game mechanics but also economic processes.

Platform-In-Game Tokenomics
Key Elements of P2E Tokenomics
- Token Creation: This process includes the issuance of new tokens by game developers and determining their initial value. It is important to balance the number of tokens issued to avoid hyperinflation.
- Token Distribution: Developers can use various methods to distribute tokens among players: from rewards for winning matches to completing quests or other tasks.
- Token Usage: Tokens can be used to buy in-game items, pay entry fees for tournaments, or exchange for real money through cryptocurrency exchanges.
- Long-Term Sustainability: A key aspect is maintaining the long-term sustainability of tokenomics. This includes controlling inflation, implementing mechanisms that prevent token depreciation, and keeping players interested in the game.
Tokenomics Models
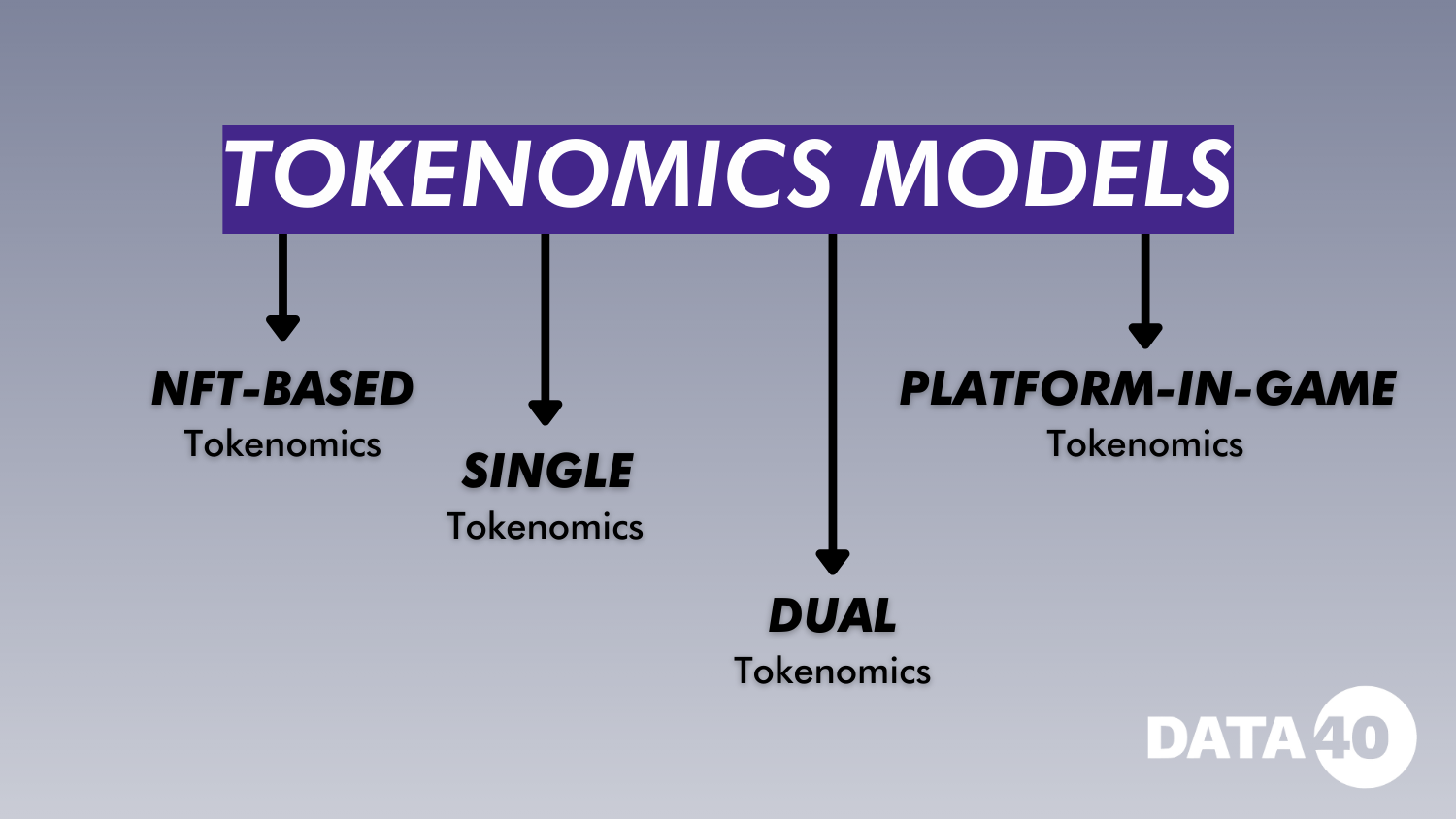
- NFT-Based Tokenomics:
The first wave of blockchain games, such as CryptoKitties, introduced a tokenomics model based on NFTs. In this model, the main focus is on ownership of game items, which simplifies economic management but creates dependence on external factors, such as fluctuations in the prices of mainnet tokens. This model is suitable for P2E games that do not require a complex economy and are focused on collecting. - Single Tokenomics:
The single tokenomics model, where one token serves both in-game and governance functions, has gained widespread use in projects such as Axie Infinity and Decentraland. However, it is vulnerable to asset outflows when users or investors withdraw their tokens from the game. In such cases, token value can fluctuate significantly, leading to economic instability in the game. - Dual Tokenomics:
To minimize asset outflow, the dual tokenomics model was developed, first applied in Axie Infinity. This model uses two tokens: one for in-game operations and the other for governance. This structure allows better control of inflation and stabilizes the economy, but it is also subject to risks associated with token listing on exchanges, which can lead to economic collapse, as happened with Axie Infinity and STEPN. - Platform-In-Game Tokenomics:
This model, introduced by platforms like Wemix and MarbleX, allows several in-game tokens to be managed under one platform token. Platform-in-game tokenomics was first applied to create more sustainable and independent economic systems in games, as well as to give players the ability to own and manage their in-game assets independently of developers. This model is becoming a standard among major gaming companies, especially in South Korea, thanks to its ability to combine the value of multiple games.
How to Choose the Right Economic Model
The choice of tokenomics model depends on the game’s genre, its lifespan, and the presence of popular IP. This means that game developers choose the tokenomics model based on several key factors:
- Game Genre: Different genres may use different tokenomics models: for example, collectible games may remain on the NFT model, while casual games prefer single tokenomics. AAA-level games that require a complex economy are likely to choose dual tokenomics or a hybrid model.
- Game Lifespan: Games with a short lifecycle, such as seasonal games, may use simpler tokenomics, while long-term projects like MMORPGs will require more complex and sustainable economic models.
- Presence of Popular IP (Intellectual Property): If the game is based on a well-known brand or franchise (e.g., popular movies, series, or other games), this may influence the choice of tokenomics model. Known IPs can attract more users and create high demand for tokens, which will require a special approach to managing the economy.
Thus, the choice of economic model cannot be universal but should adapt to the features of each game.
To create sustainable tokenomics in P2E games, developers need to conduct deep analysis of economic models and market needs, enlist the support of specialists, and adhere to such aspects as asset outflow and the role of governance tokens; a gradual transition to an open economy, ensuring the stability and sustainability of the in-game economy.
Professional Recommendations for Web3 Game Development:

- Gradual Transition to an Open Economy
One of the key aspects shaping the future of Web3 game tokenomics is the gradual transition from the closed economy typical of Web2 games to the open economy of Web3. This transition can be implemented by gradually introducing tokenomics elements, such as NFTs, in-game tokens, and governance tokens, once the game reaches a certain scale and stability. This approach will minimize the impact of early speculative demand on the in-game economy and reduce risks associated with sharp token price fluctuations. - Strengthening the Role of Governance Tokens
Governance tokens should be used not only for voting and decision-making on project development but also for active participation in the in-game economy. For example, the ability for players to use governance tokens to enhance in-game assets, participate in server resource distribution, or influence other aspects of the game. This approach fosters closer integration of gameplay and tokenomics, giving players more engagement and control over their gaming experience.
Inflation Management
Inflation is one of the main threats to Web3 game tokenomics. Developers should implement more sophisticated inflation management mechanisms, such as automatic token burning, dynamic emission regulation, and the use of algorithmic models to maintain in-game currency stability. For example, in-game events or actions requiring significant token expenditures can be used to control the number of tokens in circulation and prevent hyperinflation.
- Burn-to-Earn Model
Description: This model involves burning a certain portion of tokens when certain actions or goals are achieved in the game, increasing the value of the remaining tokens.
Advantages: Reduces token inflation and increases scarcity, which can drive up token prices.
Disadvantages: Requires careful management of the number of tokens burned to avoid a deficit and, consequently, a liquidity crisis. - Stake-to-Earn Model
Description: Players can stake their tokens for a certain period and receive rewards in the form of additional tokens or other in-game assets.
Advantages: Increases player loyalty and reduces the number of tokens in circulation, stabilizing their value.
Disadvantages: Raises the barrier to entry since players need to have tokens in advance for staking.
These models can be integrated as supplements to the main economy, enhancing player engagement and creating additional incentives for participation.
Hybrid Monetization Models
Creating hybrid monetization models that combine elements of P2E, freemium, and subscriptions allows developers to offer players various monetization and engagement paths while maintaining a sustainable game economy. For example, players can choose between earning tokens by completing specific tasks or purchasing premium accounts with extended features.
Improved Decentralization and Self-Governance
One of the main goals of Web3 is to create decentralized ecosystems where governance is carried out by the community. Self-governance mechanisms, such as DAOs (decentralized autonomous organizations), allow players to directly influence game development, vote for changes, and participate in resource allocation. This enhances user engagement and gives them the opportunity to learn to work with Web3 technologies and mechanisms like decentralization and tokenomics.
Tokenization of Off-Game Assets
With the development of Web3, game tokenomics includes not only in-game assets but also the tokenization of off-game resources. This development could include creating and trading virtual real estate, integrating with social networks and other online platforms, and using tokens to purchase real goods and services. This approach will contribute to the further expansion of the game world’s boundaries and increase the value of tokens.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendliness
Web3 game tokenomics also pays attention to environmental sustainability. With the rise of blockchain projects, there is a need to reduce energy consumption and minimize negative environmental impacts. New technologies, such as more energy-efficient blockchains or transitioning to Proof-of-Stake models, contribute to creating more environmentally friendly and sustainable game ecosystems.
The Future of Tokenomics
This article illustrates how the evolution of tokenomics in games—from NFT-based models to platform-in-game tokenomics—reflects changes in the approach to creating game economies. Considering current trends and challenges, it is possible to predict that the future of P2E games will rely on complex and flexible tokenomics models that take into account both in-game needs and investor interests.
P2E game tokenomics is constantly evolving, and each new model brings its own advantages and challenges. For gaming companies to successfully transition from Web2 to Web3, they must learn from the past and develop new approaches to economic management that consider the unique features of Web3’s open economy.
The future of Web3 game tokenomics promises to be exciting and full of new opportunities for both players and developers. With the development of new technologies and monetization models, the gaming industry is moving to a new level, where decentralization, self-governance, and sustainable development will become key principles. These changes open new horizons for creating more complex, stable, and fair game economies, providing participants with maximum immersion and long-term engagement.